#1. Cache Requests
Caching is one of the best ways to improve API performance. If you have requests that frequently produce the same response, a cached version of the response avoids excessive database queries. The easiest way to cache responses is to periodically expire it, or force it to expire when certain data updates happen.
For example, suppose you have a stock quote API that provides end-of-day stock prices. Since the response (e.g. the stock price) only changes once at 4:00pm EST each day (when the market closes), you can cache the response the rest of the time. This avoids making database queries to return the unchanged stock price.
#2. Prevent Abuse
You’re probably aware of distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, but there are far more cases of accidental abuse. For example, a developer using your API on a local application may accidentally execute a loop, causing a sudden burst of requests that slow down your performance. It could even be deployed into production!
The best way to avoid these problems is to implement a rate-limiting strategy. By measuring the number of transactions per second, per IP address, or token (if each client is authorized before accessing the API), you can cut off API clients that make excessive requests and prevent DDoS-like slowdowns from accidentals.
#3. Use PATCH
Many developers believe PUT and PATCH are essentially the same methods, but in reality, they both update a resource in different ways. PUT requests modify a resource by sending updates to the entire resource, whereas PATCH applies a partial update to it. The latter has a smaller payload that can improve performance in some cases.
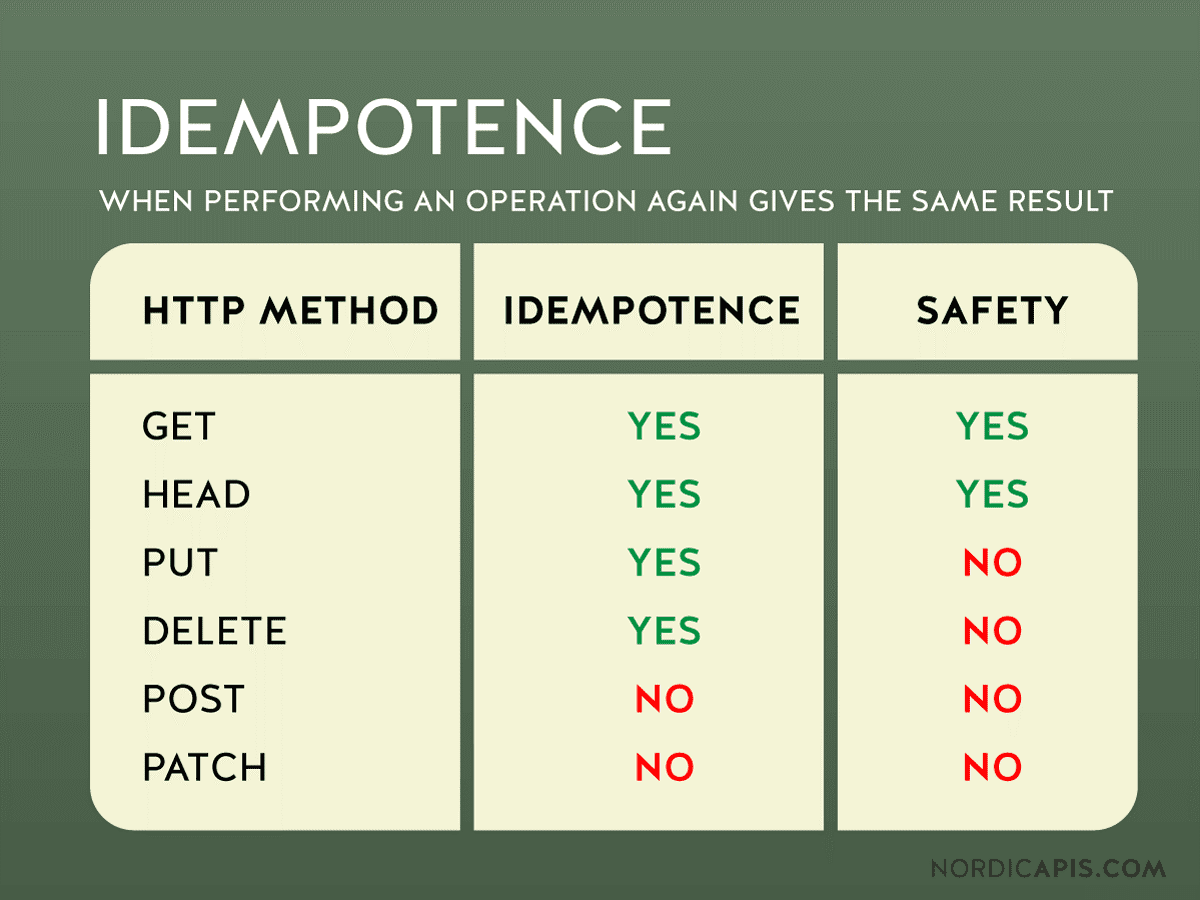
Idempotency via Request Type – Source: Nordic APIs
While PATCH can reduce the size of each request, note that it’s not idempotent, which means it can yield different results with multiple requests. Carefully consider your use case for PATCH requests and ensure they’re idempotently built if needed, or use PUT requests in those cases.
#4. Limit Payloads
Most APIs don’t have very large payloads, but there are some exceptions to the rule. For example, an analytics company may need to return a year’s worth of data. These large payloads can take a long time to create on the server and even longer to download on a client, which means that they’re usually best transferred in a compressed format.
You can reduce the size of a payload by compressing it with gzip – just modify the `Accept-Encoding` header to `gzip`. The client may spend a bit more CPU power to decompress the file, but it’ll reduce the download size, and may be worth the trade-off. Alternatively, you can use GraphQL to enable clients to request only the data they need from the server.
#5. Faster Network
Slow networks impact the performance of even the best designed APIs. Even worse, unreliable networks can cause outright downtime that could cause you to violate terms of service or other promises made to your API clients. It’s always a good idea to invest in the right infrastructure so you can maintain the right level of performance.
You can solve network-related performance issues by using reputable hosts and purchasing sufficient cloud infrastructure (e.g. enough CPUs or database instances). If you have a lot of background tasks, you should run those on separate threads/jobs to avoid blocking requests. You should also use mirrors or CDNs to serve requests faster around the world.
Ensuring Performance With LoadNinja
LoadNinja has become one of the most well-known browser-based load testing tools for web applications, and now provides a robust solution for load testing APIs. By combining these two tools in a single platform, you can run all of your load tests in one place rather than learning multiple performance tools.
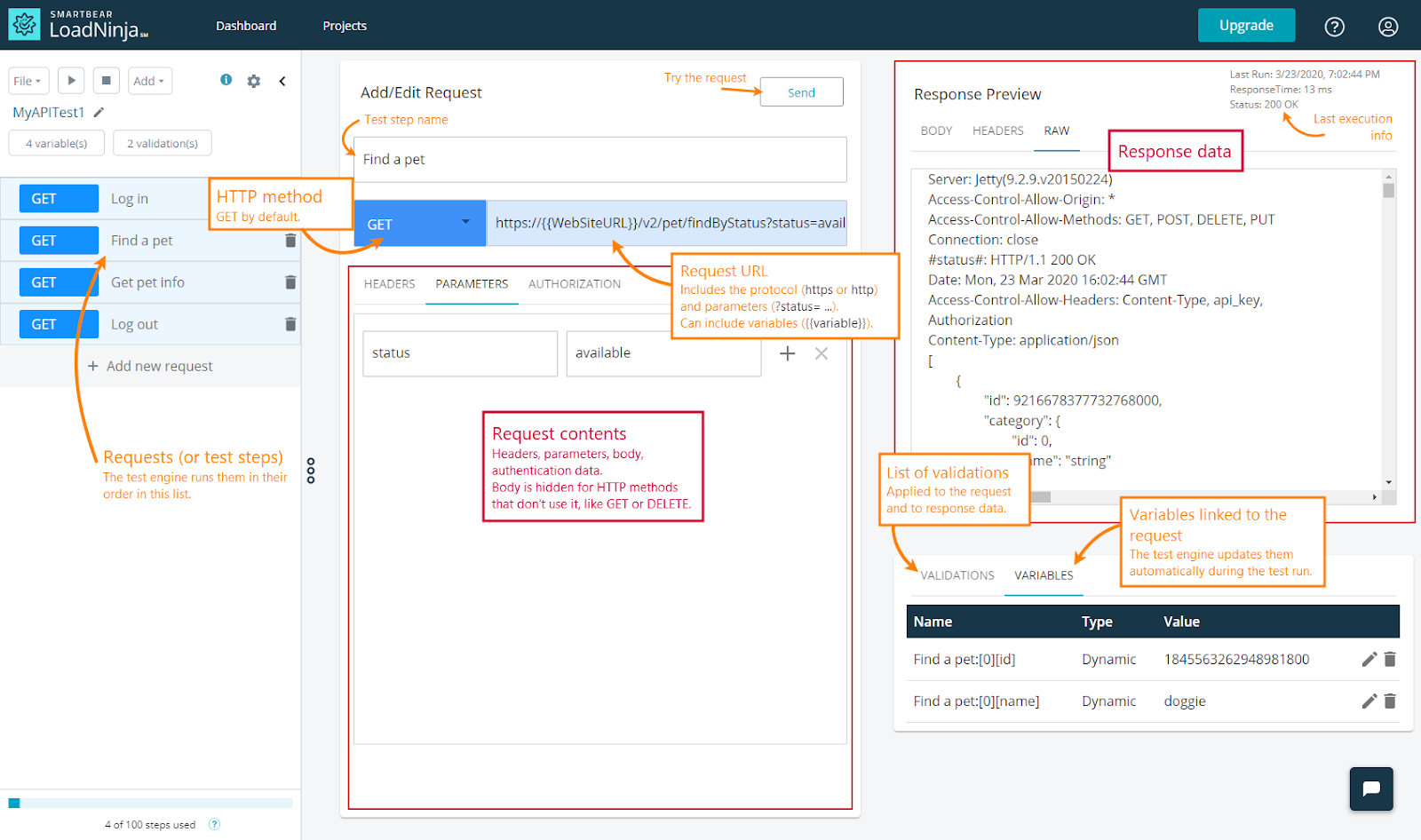
LoadNinja API Testing Platform – Source: LoadNinja
In addition to convenience, LoadNinja’s API load testing suite makes it easy to build load tests using a web-based user interface rather than diving into code. You can easily connect load tests to your existing CI/CD platform and troubleshoot any errors using its robust toolset. It’s the easiest and most efficient way to ensure you have a robust performance test suite.
Sign up for a free trial
See how easy it is to get started!
Small Steps to Reliable Performance
APIs are the lifeblood of modern software companies, which means they should be fast and reliable. By making a few simple performance optimizations, you can significantly cut down on response times and ensure consistent uptime. The key is including these optimizations in your development cycle rather than trying to find time to make them ad hoc.
In addition to these optimizations, you should integrate API performance tests into your existing continuous integration and deployment test suites. The easiest way to do this is using all-in-one browser-based performance testing frameworks, like LoadNinja, that lower the learning curve and make it easy to increase test coverage.
Sign up for a free trial of LoadNinja
Give it a Try